Best Medications for Alzheimer’s Patients
One of the problems when it comes to the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease is that we still do not know what causes it. Therefore, we have no treatments that can cure the condition. So far, all the best medications for Alzheimer’s patients only manage the below symptoms to some extent.

Alzheimer’s disease is a very complex disorder that has many components, which include the following:
- Chronic loss of memory
- Abnormal or distorted thinking
- Paranoia
- Delusions
- Agitation, anger, and irritability
- Depression
- Wandering or restless pacing
- Disinhibited behavior, like saying inappropriate things or doing inappropriate things
- Sleep disturbances
Because the above symptoms can be severe and cause a great deal of distress among caregivers, some type of treatment is necessary. For most of the above symptoms, the first choice of treatment is non-medical therapy. It is only when the non-medical treatments fail that one should consider prescription medications.
In general, prescription drugs should not necessarily be the first choice, as they also can have adverse side effects. What are the pros and cons of Alzheimer’s medication? They can curb symptoms and prolong the quality of life for some, but the drugs do not work for everyone, and their benefits do not last forever.
Once non-drug treatments have been tried and do not work, then drug treatment may be the only viable option. Some of the best medications for Alzheimer’s patients include the following.
ANTIPSYCHOTIC DRUGS
Antipsychotic drugs are also sometimes referred to as neuroleptics. These medications were developed to manage schizophrenia and other illnesses that can cause psychotic symptoms. They are very efficient at managing delusions, paranoia, anger, aggressiveness, and impulsive behavior. Common antipsychotics used to manage behavior include:
- aripiprazole (Abilify)
- asenapine (Saphris)
- cariprazine (Vraylar)
- clozapine (Clozaril)
- lurasidone (Latuda)
- olanzapine (Zyprexa)
- quetiapine (Seroquel)
- risperidone (Risperdal)
- ziprasidone (Geodon)
Haloperidol (brand name Haldol) is usually used to treat acute episodes like anger, aggressiveness, and self-harm.
POSSIBLE SIDE EFFECTS
However, antipsychotics can also have potential adverse side effects, which include the following:
- Blurred vision
- Dry mouth
- Drowsiness
- Muscle spasms or tremors
- Weight gain
ADDITIONAL ADVERSE SIDE EFFECTS FROM HIGH DOSAGE
When the dose of the antipsychotic drug is high, the following additional adverse side effects can occur:
- Increased risk of a fall
- Diminished cognitive function
- High risk of stroke and death
- Movement disorders known as extrapyramidal symptoms; can mimic symptoms like that of Parkinson’s disease
The pros and cons of Alzheimer’s medications include the fact that antipsychotics may decrease psychotic symptoms, such as paranoia, hallucinations, or delusions, but it is rare for them to completely correct these symptoms in AD patients. Antipsychotic drugs are best started at the lowest dose possible and gradually increased until a response is seen. They take about 2-4 weeks to fully work and have to be continued as long as the symptoms last.
BENZODIAZEPINES
This class of medications is sometimes used to manage sleep problems, anxiety, anger, and stress. Benzodiazepines are very effective medications and work immediately. The problem with these medications is that they can be addictive and also have side effects, like sedation. Commonly used benzodiazepines include:
- alprazolam (Xanax)
- chlordiazepoxide (Librium)
- clonazepam (Klonopin)
- clorazepate (Tranxene)
- diazepam (Valium)
- estazolam (Prosom)
- flurazepam (Dalmane)
- lorazepam (Ativan)
The benzodiazepines are only used for short periods of time that vary from a few days to a few weeks at most. While they do induce a state of relaxation and provide good sleep, they do not reverse the memory deficits. The lowest dose is used, and short-acting benzodiazepines are preferred.
POSSIBLE SIDE EFFECTS
Side effects of benzodiazepines include:
- Higher risk of falls
- Increased sedation
- Worsening confusion
- Paradoxical agitation
- A rapid decline in cognitive function
Sudden withdrawal of these agents can increase anxiety. While the benzodiazepines do work, their use should be limited to a few days to avoid the side effects.
MOOD STABILIZERS
The best medications for Alzheimer’s patients can include mood stabilizers and anti-seizure medications. Over the past two decades, drugs used to manage seizures have also been found to be excellent at modulating mood, and hence they are also referred to as mood stabilizers. Common mood stabilizers include:
- Carbamazepine (Tegretol)
- Divalproex sodium (Depakote)
- Lamotrigine (Lamictal)
- Lithium
- Valproic acid (Depakene)
These drugs are efficacious for the management of behavior problems in dementia. Some healthcare providers prefer to use mood stabilizers when the patient is not able to tolerate antipsychotics.
POSSIBLE SIDE EFFECTS
However, mood stabilizers also have adverse side effects, which can include the following:
- Dizziness
- Confusion
- Difficulty concentrating
- Difficulty with gait and balance
- Tremor
- Gastrointestinal symptoms, like nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea
Even though these drugs do not reverse dementia, they are sometimes used to manage behavior problems in select patients with Alzheimer’s disease.
ANTIDEPRESSANTS
One very common mood problem in Alzheimer’s patients is the development of depression, which can be quite severe. To reverse the depression, sometimes antidepressants are used. These drugs have several other actions besides just reversing depression; they can ease pain, provide excellent sleep, and relieve anxiety. The antidepressants do not work right away and often take 3-4 weeks to reach maximum benefit. Common antidepressants include:
- sertraline (Zoloft)
- fluoxetine (Prozac, Sarafem)
- citalopram (Celexa)
- escitalopram (Lexapro)
- paroxetine (Paxil, Pexeva, Brisdelle)
- fluvoxamine (Luvox)
POSSIBLE SIDE EFFECTS
The antidepressants also have side effects that include the following:
- Sedation
- Mouth dryness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Low blood pressure
- Risk of falls
- Worsening of agitation
Elderly people are generally very sensitive to antidepressants and only the smallest dose of the drug should be used. While they may provide good sleep and reverse depression, their use is discouraged because of the side effects.
DRUGS TO MANAGE DEMENTIA
Over the past three decades, several drugs have been developed to manage the thinking and memory problems seen in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. These include the best medications for Alzheimer’s patients to date. Overall, these drugs do help with some neuropsychiatric problems but only in the mild stage of the disease. Known as cholinesterase inhibitors, the drugs include:
- Donepezil (Aricept)
- Galantamine (Razadyne, Reminyl)
- Rivastigmine (Exelon)
Some patients with AD do obtain benefits from these drugs, such as better concentration, decreased anxiety, and more motivation, and some are even able to maintain their regular daily activities. But these improvements usually only last 6-12 months. Their main benefit is that they delay disease worsening for some time.
POSSIBLE SIDE EFFECTS
The adverse side effects of cholinesterase inhibitors include:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Diarrhea
- Muscle cramps
- Easy bruising
- Headaches
- Insomnia
- Fatigue
MEMANTINE
The best medication for Alzheimer’s patients might be Memantine. It is another drug used to treat the late stages of Alzheimer’s disease. The drug has been shown to improve attention, memory, and language in some patients. It is often prescribed with the drug donepezil (Aricept) for maximum benefit. Memantine works by balancing the brain neurotransmitters involved in language and memory. Studies show that memantine can reduce delusions, paranoia, confusion, and hallucinations, but, again, the benefits are not sustained for more than a few months.
POSSIBLE SIDE EFFECTS
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Constipation
- Fatigue
- Confusion
- Insomnia
- High blood pressure
NEW DRUGS
Researchers are working to find the best medication for Alzheimer’s patients. Over the past year, several new drugs have been developed to treat Alzheimer’s disease. These latest drugs are administered by injection and can dissolve the amyloid plaques in the brain. Amyloid plaques have been associated with Alzheimer’s disease and early studies indicate that by dissolving the plaques, the progression of Alzheimer’s disease can be slowed or prevented. Two monoclonal antibodies have been approved by the FDA to break down amyloid plaques in the brain: they include aducanumab and solanezumab. Several other similar drugs are currently being evaluated in clinical trials.
Early results are promising but before one can get treatment, one has to undergo a PET scan to look for plaques. Only AD patients with plaques are eligible for this treatment. The other problem with these agents is the cost, which varies from $28K to $56K. Even though Medicare will cover a significant part of the cost, all patients are left with large copayments. Finally, the long-term side effects and the pros and cons of Alzheimer’s medication drugs remain unknown.
HEART AND BRAIN CONNECTION
More evidence seems to link the brain and the heart as an extremely important connection in Alzheimer’s patients. Population studies reveal that people whose blood pressure is controlled and who lead a healthy lifestyle have a far lower risk of AD compared to populations who have high blood pressure and live an unhealthy lifestyle. Hence, the current emphasis is on adopting a positive lifestyle in the hopes of preventing AD in the first place. This means eating healthy, exercising regularly, discontinuing smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, and keeping blood pressure within normal limits. Speak to your healthcare provider if you want to know more about lowering your risk of getting diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease. Preventing AD in the first place is a far better option than treating it later.
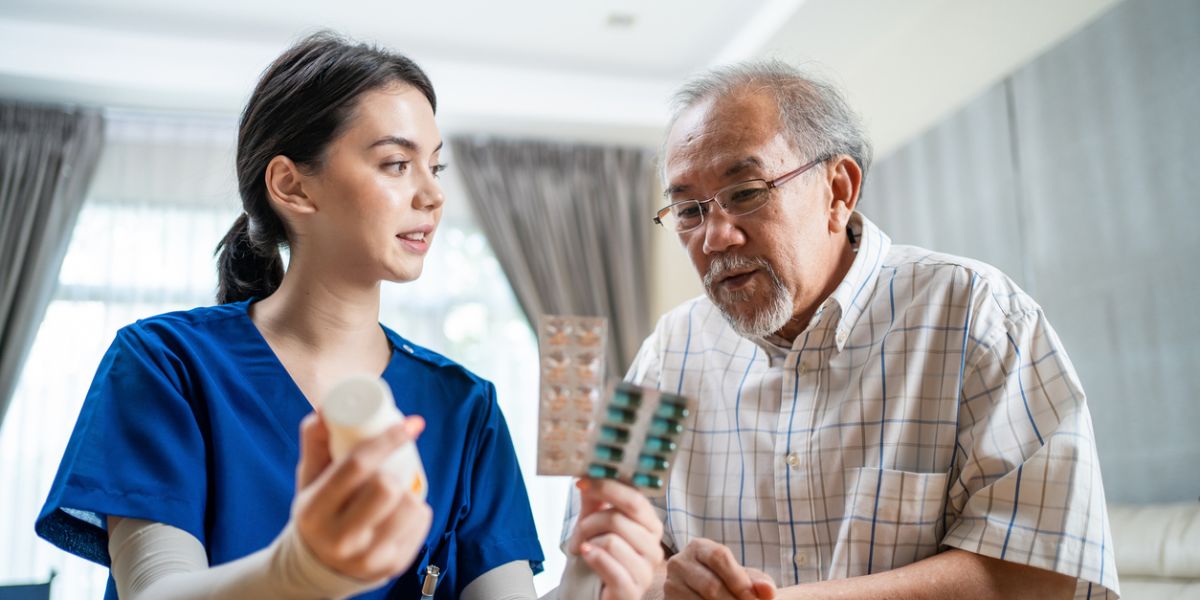
TAKING MEDICATIONS BY MOUTH
Giving medications by mouth to an AD patient can be a real challenge. For example, they may refuse or spit the pill out, or they may not swallow it at all because they do it know it is a medication. It could also be that the individual may have a physical problem that prevents swallowing. In such cases, it is important to speak to the pharmacist and obtain the medication in a liquid form, if possible. Another option is to break the pill in half or open the capsule and sprinkle the powder into food or a beverage.
CONCLUSION
Medical advances in technology and new options for treating diseases are made every day. It is important to stay on top of the latest information about the best medications for Alzheimer’s patients, as well as the pros and cons of Alzheimer’s medications. Cano Health wants you to have the best life possible and they are committed to providing excellent care to their members and senior patients. If you would like to learn more about how Cano Health can make a significant impact in your life, call them today at 1-855-208-7874.